Exploring Bonsai Aesthetics: Generating Visual Depth and Opposing Elements
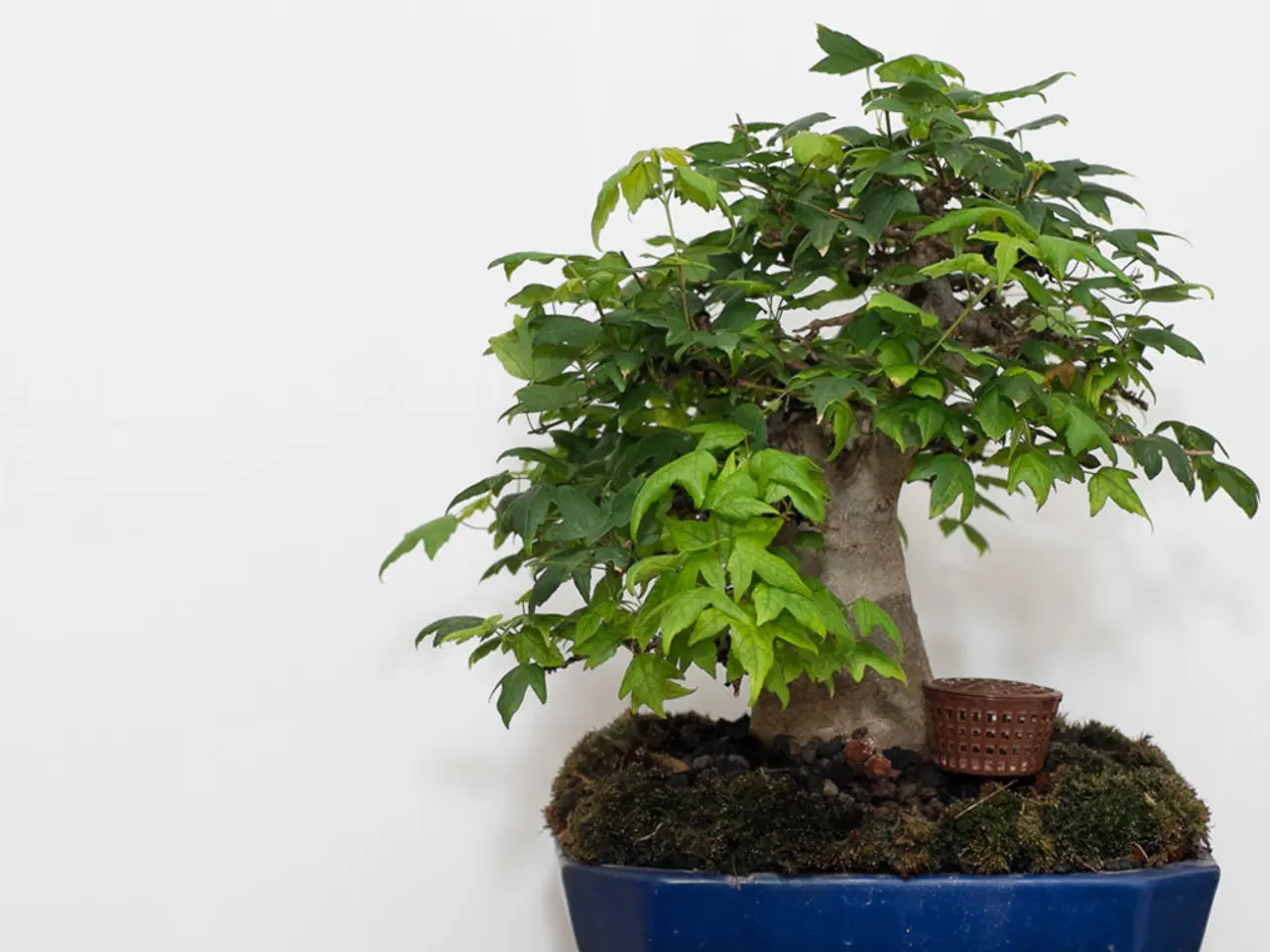
Bonsai, the ancient art of growing miniature trees, offers a unique opportunity to appreciate the intricate beauty of nature in a compact form. One key aspect that sets bonsai apart is the deliberate use of texture and contrast in its design.
To safeguard a bonsai's texture from extreme weather conditions, protective measures such as sheltering, breathable covers, misting, and humidity control are employed. However, it is in the careful combination of varying surface qualities and visual elements that bonsai designers truly create depth, highlight details, and enhance interest in their compositions.
The inherent variability of tree species offers a rich tapestry of textures, from rugged, fissured bark to smooth, silver-gray skin. Bonsai artists masterfully use this diversity, contrasting rough bark textures with soft or smooth elements like moss or a simple pot surface. This juxtaposition invites the viewer's eye to dance between contrasting textures, heightening visual interest.
Placing bonsai against contrasting backdrops, such as dark fences or textured walls, makes the fine details of the tree stand out vividly, especially under lighting, which enhances texture and creates dramatic visual contrasts. Designers also use asymmetry rather than perfect symmetry, creating natural imbalances that add dynamic tension and visual intrigue.
Grouping bonsai trees of different species and heights establishes a contrast in shapes and textures and can mimic miniature forests for more complex visual narratives. In moderation, judiciously chosen artificial elements can augment texture and contrast in bonsai, but beware of overpowering the organic essence.
Strategic incorporation of bonsai techniques like carving and pruning can enhance this interplay, adding depth and dimension. Skilled artisans may employ carving techniques to accentuate the natural textures of the tree, subtly enhancing the visual drama of the composition.
The art of bonsai texture and contrast lies in striking a delicate balance between visual interest and overall harmony of the composition. The thoughtful integration of natural elements such as rocks, moss, and lichens further enriches the textural landscape of the bonsai.
Certain bonsai species, such as ficus and juniper, are more susceptible to pest damage that can affect texture, while others like pine and spruce tend to be more resistant. To prevent texture-damaging drying out, water your bonsai when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch, usually every 2-3 days in summer and every 4-5 days in winter.
Lastly, when transferring your bonsai to its new pot, care must be taken to avoid scratching or scraping its delicate textures. The masterful interplay of texture and contrast in bonsai design creates a visually stunning experience that invites contemplation and appreciation, evoking the intricate beauty of the natural world in miniature.
- To complement the intricate beauty of bonsai, strategic placement of contrasting backdrops, like dark fences or textured walls, and intentionally incorporating lighting helps make the fine details of the tree stand out even more.
- The deliberate juxtaposition of rough bark textures with soft or smooth elements like moss or pot surfaces enhances visual interest, inviting the viewer's eye to dance between contrasting textures.
- Grouping bonsai trees of different species and heights not only forms miniature forests but also creates contrast in shapes and textures, enriching the visual narrative.
- In the process of creating a bonsai, protective measures like sheltering, breathable covers, misting, and humidity control are taken to conserve and safeguard the tree's texture from extreme weather conditions.